The world of custom apparel and promotional products has evolved dramatically over the past few decades, with printing screen techniques continuing to dominate certain market segments while digital printing technologies rapidly gain ground. Understanding the fundamental differences between these two printing methodologies is crucial for business owners, manufacturers, and entrepreneurs looking to make informed decisions about their production processes. The choice between printing screen methods and digital alternatives can significantly impact production costs, quality outcomes, and operational efficiency.
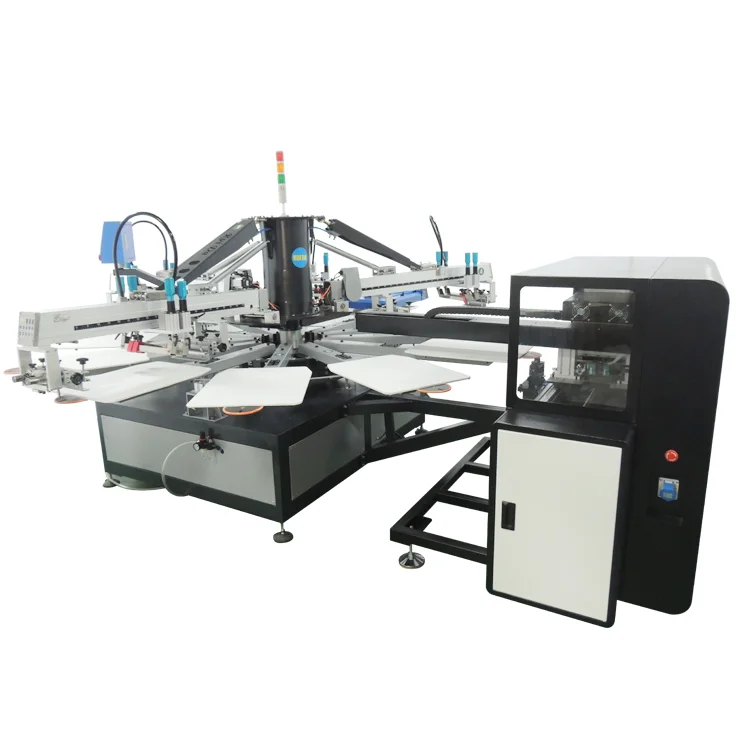

Understanding Screen Printing Fundamentals
The Traditional Printing Screen Process
Printing screen technology represents one of the oldest and most reliable methods for transferring designs onto various substrates, particularly textiles. This process involves creating a stencil, known as a screen, through which ink is pressed onto the target material using a squeegee. The printing screen method requires careful preparation of mesh screens, typically made from polyester or nylon, which are stretched over frames and coated with light-sensitive emulsion. When exposed to light through a film positive of the desired design, the emulsion hardens everywhere except where the design blocks the light, creating open areas through which ink can pass.
The traditional printing screen approach excels in producing vibrant, durable prints with excellent color opacity and longevity. Each color in the design requires a separate screen, making this method particularly cost-effective for large production runs where the setup costs can be distributed across many units. The thick ink deposits achieved through printing screen techniques result in prints that can withstand numerous wash cycles while maintaining their original appearance and feel.
Equipment and Setup Requirements
Modern printing screen operations require substantial initial investment in equipment, including screen frames, squeegees, inks, emulsion chemicals, and curing systems. Professional printing screen setups often feature automatic or semi-automatic presses that can handle multiple colors simultaneously, significantly increasing production efficiency. The process demands skilled operators who understand ink viscosity, screen tension, squeegee pressure, and curing temperatures to achieve consistent results.
Temperature control plays a critical role in printing screen success, as most textile inks require heat curing to achieve proper adhesion and washability. Industrial printing screen facilities typically invest in conveyor dryers, flash cure units, and heat presses to ensure proper ink fixation. The complexity of printing screen setup means that smaller jobs may not be economically viable due to the time and materials required for screen preparation and cleanup.
Digital Printing Technologies and Applications
Direct-to-Garment Printing Methods
Digital printing has revolutionized the custom apparel industry by eliminating many of the setup requirements associated with traditional printing screen methods. Direct-to-garment (DTG) printing uses specialized inkjet technology to apply water-based inks directly onto textile fibers, creating detailed, full-color designs without the need for screens or stencils. This technology enables printing complex designs with unlimited colors, gradients, and photographic elements that would be prohibitively expensive or impossible to achieve through conventional printing screen techniques.
The digital approach offers unmatched flexibility for small batch production and on-demand manufacturing, making it ideal for personalized products, test designs, and limited edition runs. Unlike printing screen methods that require minimum quantities to be economically viable, digital printing can efficiently handle single-piece orders while maintaining reasonable per-unit costs. This capability has opened new market opportunities for custom apparel businesses and enabled just-in-time production strategies.
Sublimation and Heat Transfer Technologies
Digital sublimation printing represents another significant advancement in non-screen printing technologies, particularly effective for polyester fabrics and polymer-coated substrates. This process converts solid dye particles directly into gas phase, allowing them to penetrate synthetic fibers and create permanent, washable prints. Sublimation differs fundamentally from printing screen methods by eliminating the need for wet inks and reducing environmental impact through cleaner production processes.
Heat transfer vinyl (HTV) and printable transfer materials offer additional digital alternatives to traditional printing screen applications. These methods involve cutting designs from colored vinyl or printing onto transfer papers that are subsequently applied using heat and pressure. While lacking the durability of quality printing screen work, digital transfer methods provide excellent results for specialized applications and materials that cannot be processed through conventional printing screen equipment.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Initial Investment and Setup Costs
The financial implications of choosing between printing screen and digital printing methods vary significantly depending on production volume and business model. Printing screen equipment typically requires higher initial capital investment, with professional multi-color presses costing tens of thousands of dollars, plus ongoing expenses for screens, inks, chemicals, and maintenance. However, the per-unit cost of printing screen production decreases dramatically with volume, making it the preferred choice for large orders and repeat designs.
Digital printing equipment, while still representing substantial investment, often provides lower barrier to entry for small businesses. Entry-level DTG printers and heat transfer systems can be acquired for significantly less than complete printing screen setups, though industrial-grade digital equipment can be equally expensive. The key advantage lies in eliminated screen preparation costs and reduced waste, as digital methods only use the exact amount of ink required for each print.
Production Volume Economics
Production volume fundamentally determines the cost-effectiveness of printing screen versus digital methods. Traditional printing screen becomes increasingly economical as order quantities grow, with break-even points typically occurring around 50-100 pieces depending on design complexity and color count. Large runs of 500+ pieces almost invariably favor printing screen methods due to faster production speeds and lower per-unit ink costs.
Conversely, digital printing maintains consistent per-unit costs regardless of quantity, making it ideal for small orders, samples, and personalized products. This pricing structure enables business models focused on customization and rapid turnaround rather than volume production. The ability to efficiently process single-piece orders through digital methods has created entirely new market segments that would be unprofitable with traditional printing screen approaches.
Quality and Durability Comparisons
Print Longevity and Wash Resistance
Quality expectations play a crucial role in determining the appropriate printing method for specific applications. Professional printing screen techniques, when properly executed, produce prints that can withstand hundreds of wash cycles while maintaining color vibrancy and structural integrity. The thick ink deposits characteristic of printing screen methods create a slightly raised surface that many customers associate with premium quality. Plastisol inks commonly used in printing screen applications cure to form flexible, durable layers that move naturally with fabric stretching.
Digital printing quality has improved dramatically with advances in ink chemistry and printer technology, though durability characteristics differ from printing screen results. Water-based digital inks typically penetrate fabric fibers more deeply than printing screen deposits, creating softer hand feel but potentially less vibrant color saturation. Modern digital prints can achieve excellent wash resistance when properly pre-treated and cured, though they may not match the longevity of quality printing screen work under extreme conditions.
Color Accuracy and Design Complexity
Design complexity represents a key differentiator between printing screen and digital methods. Traditional printing screen excels at producing solid colors, simple graphics, and designs with clear color separations. Each color requires a separate screen, making complex, multi-color designs expensive and time-consuming to produce. However, the color mixing capabilities of printing screen inks allow for precise Pantone matching and specialty effects like metallic or glow-in-the-dark prints.
Digital printing shines in reproducing photographic images, gradients, and designs with unlimited color counts. The ability to print directly from digital files eliminates color separation requirements and enables rapid design modifications without additional setup costs. While digital methods may struggle to match certain specialty printing screen effects, they offer unparalleled flexibility for complex artwork and personalization requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chemical Usage and Waste Generation
Environmental considerations increasingly influence printing method selection as businesses prioritize sustainability. Traditional printing screen operations generate significant chemical waste through screen cleaning, emulsion removal, and ink disposal. The reclaiming process required to reuse printing screen frames involves harsh chemicals that must be properly managed to prevent environmental contamination. Large-scale printing screen facilities typically implement closed-loop water systems and waste treatment protocols to minimize environmental impact.
Digital printing generally produces less chemical waste, particularly when using water-based inks and eco-friendly pretreatment solutions. The elimination of screen cleaning chemicals and reduced ink waste contribute to cleaner production processes. However, digital printing relies heavily on electricity for printer operation and heat curing, potentially offsetting some environmental benefits depending on local energy sources.
Energy Consumption and Carbon Footprint
Energy usage patterns differ significantly between printing screen and digital methods. Printing screen operations require substantial energy for ink curing, typically using gas-powered conveyor dryers or electric flash cure units. However, the high production speeds achievable with automated printing screen equipment can result in lower energy consumption per unit for large runs. The thermal mass of printing screen curing equipment means energy efficiency improves with continuous operation.
Digital printing energy requirements center around printer operation, pretreatment processes, and heat pressing or curing. While individual print energy consumption may be higher for digital methods, the elimination of setup waste and ability to print only what is needed can reduce overall environmental impact for small-scale production. The growing availability of renewable energy sources makes digital printing increasingly attractive from a carbon footprint perspective.
Market Applications and Industry Preferences
Commercial and Industrial Applications
Different market segments show distinct preferences for printing screen versus digital methods based on specific requirements and constraints. The promotional products industry relies heavily on printing screen techniques for producing large quantities of branded merchandise, taking advantage of consistent quality and competitive pricing for volume orders. Corporate uniform suppliers typically prefer printing screen methods for their ability to match exact brand colors and produce durable prints that maintain professional appearance through extensive wear and washing.
Athletic and performance apparel manufacturers often utilize printing screen methods for team uniforms and sporting goods, where durability and color vibrancy are paramount. The ability of printing screen inks to flex with athletic fabrics without cracking makes this method ideal for sportswear applications. Specialty printing screen techniques like puff printing, gel printing, and metallic effects remain popular in fashion and streetwear markets where unique textures and appearances are valued.
Emerging Market Trends and Opportunities
Digital printing adoption continues expanding in markets traditionally dominated by printing screen methods, driven by consumer demand for customization and rapid fulfillment. Print-on-demand services leverage digital technology to offer unlimited design options without inventory risk, creating new business models impossible with traditional printing screen approaches. The rise of e-commerce and social media marketing has increased demand for small-batch custom products that digital methods can efficiently serve.
Hybrid approaches combining printing screen and digital technologies are gaining popularity as equipment manufacturers develop integrated solutions. These systems may use printing screen methods for base colors and digital printing for detailed elements, optimizing the strengths of both technologies. Such innovations suggest that future printing operations may not choose exclusively between methods but rather integrate multiple technologies to serve diverse customer requirements efficiently.
Technology Integration and Future Developments
Automation and Production Efficiency
Modern printing screen equipment increasingly incorporates digital controls and automation features that bridge traditional and digital printing approaches. Computer-controlled printing screen presses can automatically adjust registration, squeegee pressure, and ink flow to maintain consistent quality throughout production runs. These advancements reduce labor requirements and minimize human error while maintaining the fundamental advantages of printing screen technology.
Digital printing continues evolving through improvements in print head technology, ink formulations, and software integration. Advanced color management systems ensure consistent output across multiple printers, while automated pretreatment and curing systems reduce manual intervention requirements. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms enables predictive maintenance and quality optimization that further enhances digital printing reliability and efficiency.
Material Science and Ink Development
Ongoing research in ink chemistry benefits both printing screen and digital applications through development of more durable, environmentally friendly, and versatile formulations. New printing screen ink systems offer improved stretchability for athletic wear while maintaining excellent opacity and wash resistance. Specialty printing screen inks incorporating antimicrobial properties, moisture-wicking capabilities, and temperature-responsive characteristics expand application possibilities.
Digital ink development focuses on achieving printing screen-like durability while maintaining the soft hand feel and detail reproduction advantages of digital methods. Nano-pigment technologies and polymer-enhanced formulations promise to close the durability gap between digital and printing screen methods. These advances may eventually eliminate the trade-offs between print methods, allowing selection based purely on economic and production efficiency considerations.
FAQ
Which printing method is more cost-effective for small orders?
Digital printing is typically more cost-effective for small orders under 50 pieces because it eliminates screen setup costs and allows for efficient single-piece production. Printing screen methods require significant setup time and materials for each color, making small orders expensive due to high per-unit setup costs that cannot be distributed across many pieces.
How do print quality and durability compare between the two methods?
Printing screen generally produces more durable prints with better wash resistance and color vibrancy, especially for solid colors and simple designs. Digital printing offers superior detail reproduction and unlimited color capabilities but may have slightly less durability. Modern digital inks have significantly improved durability, making both methods suitable for most applications when properly processed.
What are the environmental implications of each printing method?
Digital printing typically generates less chemical waste and allows for more precise ink usage, reducing environmental impact for small production runs. Printing screen operations produce more chemical waste through screen cleaning and preparation but may be more energy-efficient for large volume production. Both methods can be environmentally responsible when proper waste management and energy efficiency practices are implemented.
Can both methods be used together in the same production facility?
Yes, many successful printing operations utilize both printing screen and digital methods to serve different market segments and order types effectively. This hybrid approach allows businesses to optimize production efficiency by using printing screen for large volume orders and digital methods for small batches, samples, and complex designs. Some advanced equipment even combines both technologies in single integrated systems.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Screen Printing Fundamentals
- Digital Printing Technologies and Applications
- Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
- Quality and Durability Comparisons
- Environmental Impact and Sustainability
- Market Applications and Industry Preferences
- Technology Integration and Future Developments
- FAQ